간단한 이더리움 스마트 컨트랙트를 구현해보자.

-> remix IDE 검색해 가장 먼저 뜨는 검색결과로 이동
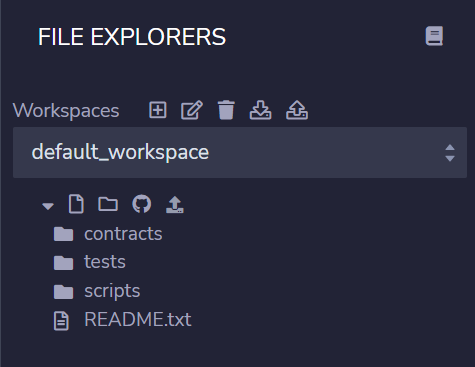
-> editor 내에서 sample contract가 담긴 default_workspace를 제공함
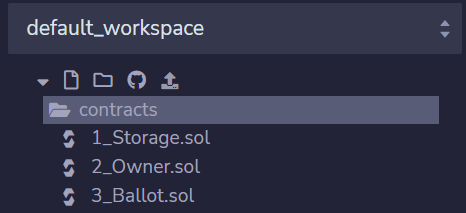
default_workspace의 contracts > 3_Ballot.sol 에 들어가서 코드 다 지우고 여기서 fresh하게 시작해보자.
* file 확장자가 .sol 임
-> solidity file을 위한 default file extension


-> contract name define
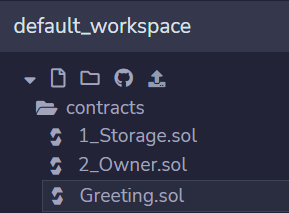
-> 파일 이름도 3_Ballot.sol에서 Greeting.sol로 rename 해줌

-> declare some state variables
these variables that will be stored on the blockchain
; exist / persist between multiple invocations or calling of the smart contract code
-> declare the type of the variable : public
* public이 아니라 private으로 정의해 뒀어도 still visible
-> 왜냐면, anything on the blockchain is visible to anybody

-> define a greeting prefix
- view 뜻 = this function is not going to change any data on the blockchain
- pure 뜻 = this function is not going to change any data on the blockchain
-> 우리는 name 과 greeting을 읽어야 하므로 view를 사용하자.

-> function body : return combination of the greeting prefix and the name

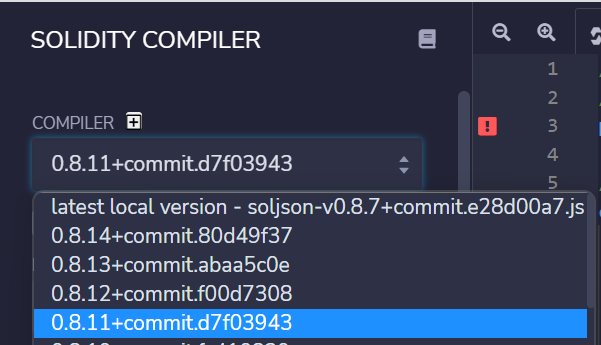
-> 컴파일러 버전 변경
참고] Data Locations - Storage, Memory and Calldata
Variables are declared as either storage, memory or calldata to explicitly specify the location of the data.
- storage - variable is a state variable (store on blockchain)
- memory - variable is in memory and it exists while a function is being called
- calldata - special data location that contains function arguments
-> actual data type(string) 옆에 data location type(memory) 적어주기
<smart contract complete code>
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.11;
//contract name define에 대해 대문자 사용
contract Greeting {
// declare the type of variable(String) | accessible to anybody and everyone(Public)
string public name;
string public greetingPrefix = "Hello ";
//constructor function
constructor(string memory initialName){
name = initialName; //지역변수 지정
}
//pubic function이므로 다른 함수가 아무나 call 가능
function setName(string memory newName) public {
name = newName;
}
//corresponding Gather
//just return some information from the smart contract
function getGreeting() public view returns (string memory) {
//view 뜻=this function is not going to change any data on the blockchain
//helper function
//pass in the two strings that we want to concatenate
//cast it to a string
return string(abi.encodePacked(greetingPrefix, name));
}
}
deploy and test 해보자
-> see how we interact with it
compile
solidity=compile language <-> JS=read directly by the browser

-> remix editor의 Compile Greeting.sol 버튼 누르면 Compile됨
cf) compile
solidity=compile language <-> JS=read directly by the browser

-> deploy code : 이더리움 모양 아이콘으로 이동
DEPLOY & RUN TRANSACTIONS

-> 실제 블록체인 환경은 아니고 JS VM 기반 가상 블록체인 에서 smart contract deploy 함
: gas fee 등 실제로 청구 x

ACCOUNT: financial transactions 관련 코드 작성 안했기에 관련 없음
GAS LIMIT
VALUE: transaction으로 이더리움 SEND 할 때 사용

-> CONSTRUCTOR가 name argument 를 취하므로 initialName(mye)을 기입해주고 DEPLOY 버튼 클릭
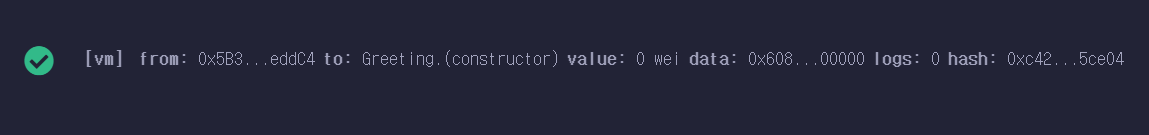
-> 정상적으로 DEPLOY 성공
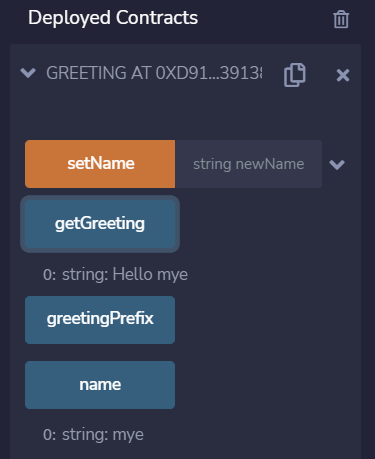
cf) define state variable 시 automatically get for free a getter function(variable과 동일한 이름)
name 클릭 시 기입한 initialName 나옴
-> getGreeting 함수에 대해서는 정의를 해줬음
-> getGreeting 클릭 시 Hello mye return됨
Test2. set new name & have that reflected in the get greeting

-> ECAC 라는 new name 기입하고 setName 클릭

-> getGreeting 클릭 시 Hello ECAC (설정한 newName이 반영되어) return됨!
[참고자료]
'PBL Ⅲ > BlockChain' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [블록체인의 원리] 5. 비트코인 스크립트 (0) | 2022.06.04 |
|---|---|
| [블록체인의 원리] 4. 비트코인의 원리 (2) (0) | 2022.06.04 |
| [블록체인의 원리] 3. 비트코인의 원리 (1) (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| [블록체인의 원리] 2. 비트코인의 탄생 (리먼 사태와 양적 완화) (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| [블록체인의 원리 ] 1. 블록 체인이란? (0) | 2022.05.24 |